Gravity is the force that pulls objects towards the centre of the Earth. It gives objects weight and causes water to flow downhill. Gravity is calculated using a gravimeter, which very precisely measures either how quickly an object falls or how much an object weighs. The New Zealand gravity networks are classified based on the method of observation, or the type of equipment used.
New Zealand’s terrestrial gravity network
New Zealand’s terrestrial gravity network has around 20,000 gravity observations that have been collected since the 1960s using portable, ground-based gravimeters. These are usually used in accessible areas like roads, river valleys and coastlines, or areas of scientific interest like the Taupō Volcanic Zone. The network has fewer observations in areas that are remote or difficult to access, such as the fiords of Southland.
This gravity network provides a consistent and precise framework for understanding variations in the gravitational field across Aotearoa. The data can be explored and downloaded through GNS Science’s Gravity Survey Data portal.
Gravity Survey Data portal - GNS Science
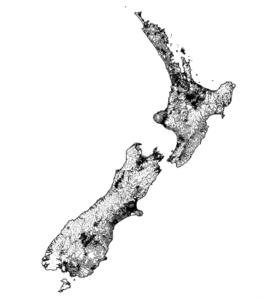
Terrestrial gravity observation points across New Zealand.
New Zealand’s airborne gravity network
The airborne gravity dataset was collected using a gravimeter mounted in an aircraft. This allows measurements to be taken over large areas, and is particularly useful in rugged and remote places where it is difficult to collect terrestrial gravity data.
Over 50,000 line-kilometres of high-resolution data was collected across New Zealand in 2014 and 2015, with the data referenced to gravity base-stations in Auckland, Hastings, Nelson and Timaru. The dataset has improved our understanding of regional gravity variations, and supports work such as geoid modelling. The full dataset can be downloaded for free through the LINZ Data Service.
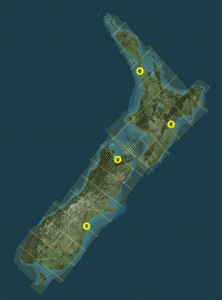
Flight lines in the airborne gravity network across New Zealand, and locations of the four base-stations.
New Zealand’s absolute gravity network
New Zealand’s absolute gravity network is a small number of precisely surveyed marks where gravity has been measured using high-precision absolute gravimeters. These directly measure gravity by tracking the fall of an object in a vacuum. Absolute gravimeter measurements are the foundation of New Zealand’s gravity reference system, making them essential for calibrating and validating other gravimeters and datasets.
Absolute gravity observation are often conducted as a matter of “opportunity”, such as the reobservation of the Southern Alps network in December 2014, and the series of measurements made in 2015 at Warkworth, Wellington, Lower Hutt, Godley Head, Mt John, and Dunedin.
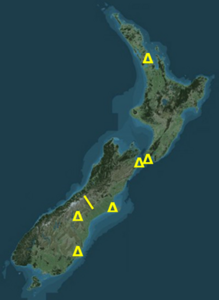
The New Zealand absolute gravity network.
New Zealand absolute gravity network observations
The tables below summarise the campaign data from the absolute gravity observation sites that contribute to the National Reference Frame in New Zealand.
Mt John - MTJG
| Year | Instrument | Gravity (μ/kg) | Uncertainty (μGAL) | Tide correction details | Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | FG5 | 980 248 935.6 | Unstated | Corrected for body tides and load tides calculated | |
| 2011 | A10 | 980 248 941 | 11 | Modelling for tides not mentioned in the report | |
| 2015 | FG5 | 980 248 931.02 | 4.9 | Modelled Earth tides and ocean tide loading using TPXO7/2 tidal model to produce a zero-tide system (IERS Convention 2010) |
Warkworth - WARG
| Year | Instrument | Gravity (μ/kg) | Uncertainty (μGAL) | Tide correction details | Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | FG5 | 979 886 253.49 | 8.18 | Modelled Earth tides and ocean tide loading using TPXO7/2 tidal model to produce a zero-tide system (IERS Convention 2010) |
Scott Base - SBG1
| Year | Instrument | Gravity (μ/kg) | Uncertainty (μGAL) | Tide correction details | Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | FG5 | 982 977 945.91 | 4.34 | Corrected for Earth tide, ocean loading, polar motion and atmospheric pressure | |
| 2015 | FG5 | 982 977 947.71 | 4.38 | Corrected for Earth tide, ocean loading, polar motion and atmospheric pressure | |
| 2018 | FG5 | 982 977 939.83 | 4.51 | Corrected for Earth tide, ocean loading, polar motion and atmospheric pressure |